Signs Your Child Has a Cavity Coronado, CA
Tooth decay, also known as dental caries or cavities, represents a common problem in childhood. Tooth decay occurs when acids produced by bacteria break down or erode the outer layer or enamel of the tooth. Luckily, cavities caught early can be easily repaired.
Pediatric dentistry is available at Coronado Dentistry & Pediatrics in Coronado and the surrounding area. We offer a range of dental and oral services for children and adolescents. Call us at (619) 435 6231 to learn more or make an appointment.
Sensitivity to Food Temperature
According to the United States Center for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), cavities remain the most common chronic disease in children between ages six and eleven and teenagers. If children complain that their teeth hurt when drinking a hot soup or eating a popsicle, parents should suspect a cavity. To understand why tooth decay may cause temperature sensitivity, it helps to consider tooth anatomy. Underneath the top enamel layer of the tooth and the cementum (which lies under the gum) remains a layer called dentin.
According to the American Dental Association, dentin has small tunnels that lead directly to the tooth’s nerve root. When the top layer of the tooth decays and exposes the dentin, hot or cold temperatures can directly impact the nerve, causing hypersensitivity.
Visible Hole, Chip, Crack, or Pit in the Teeth
Tooth bacteria appear in thin films on the teeth called plaque. Plaque covers the outer enamel layer of the teeth. Plaque can be brushed away mechanically and kept at bay with flossing and mouth washing. However, if plaque sits on the teeth surface for too long, it can begin degrading the enamel.
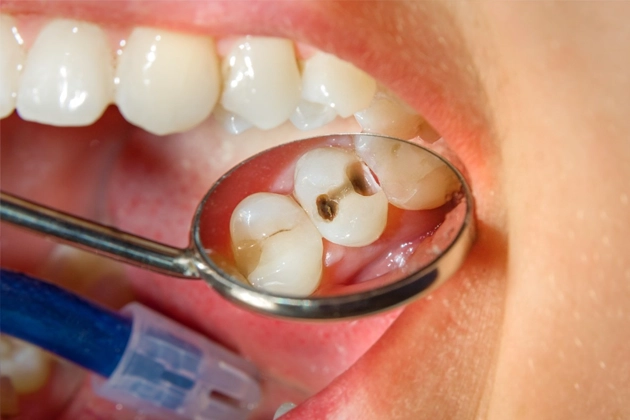
If the decay progresses far enough, it can cause visible changes. These cavities might appear as a hole, chip, crack, or pit in the teeth. In most cases, patients need to replace their natural tooth with a crown or other tooth-replacement option. Otherwise, the dentist may fill in the hole, chip, crack, or pit with a composite material and bond it to the teeth.
Gum Pain and Bleeding
Pain While Chewing
If a child has pain while chewing, this could be another sign of a cavity. Cavities represent a defect in the outer surface of the tooth. When a child chews food, small particles can enter the cavity and irritate the underlying tissues, causing pain.
According to the American Association of Endodontists, large cavities can also cause an infection of the deeper tissues of the tooth so that chewing can be painful even without lodged food particles. Large cavities require immediate attention as they can advance to become root canals if they touch the roots of the teeth. In these cases, the child will likely lose the tooth and require a root canal and crown.
Dark Spots or White Spots
A color change of a tooth may signal a cavity. As the enamel of the tooth decays, it can become discolored with either dark spots or white spots. The color change can continue as the underlying structures of the tooth, such as dentin, become exposed.
However, dark or white spots can also result from routine staining of the enamel, so it is important to have any tooth discoloration examined by a dentist. When enamel erodes, it exposes dentin, which is yellow in color, emitting that yellow-ish color. The discoloration is often due to staining agents such as coffee, tea, soda, certain juices, and smoking.